Wed, Apr 23, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 16, Issue 1 (March 2019)
IJMSE 2019, 16(1): 68-76 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Tavakoli Harandi M, Askari-Paykani M, Shahverdi H, Nili Ahmadabadi M. Effect of Casting Diameter and Heat Treatment Process on Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Fe55-XCr18Mo7B16C4NbX(X=0,3) Ribbons and Nanostructured Rods. IJMSE 2019; 16 (1) :68-76
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-1109-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-1109-en.html
Abstract: (21502 Views)
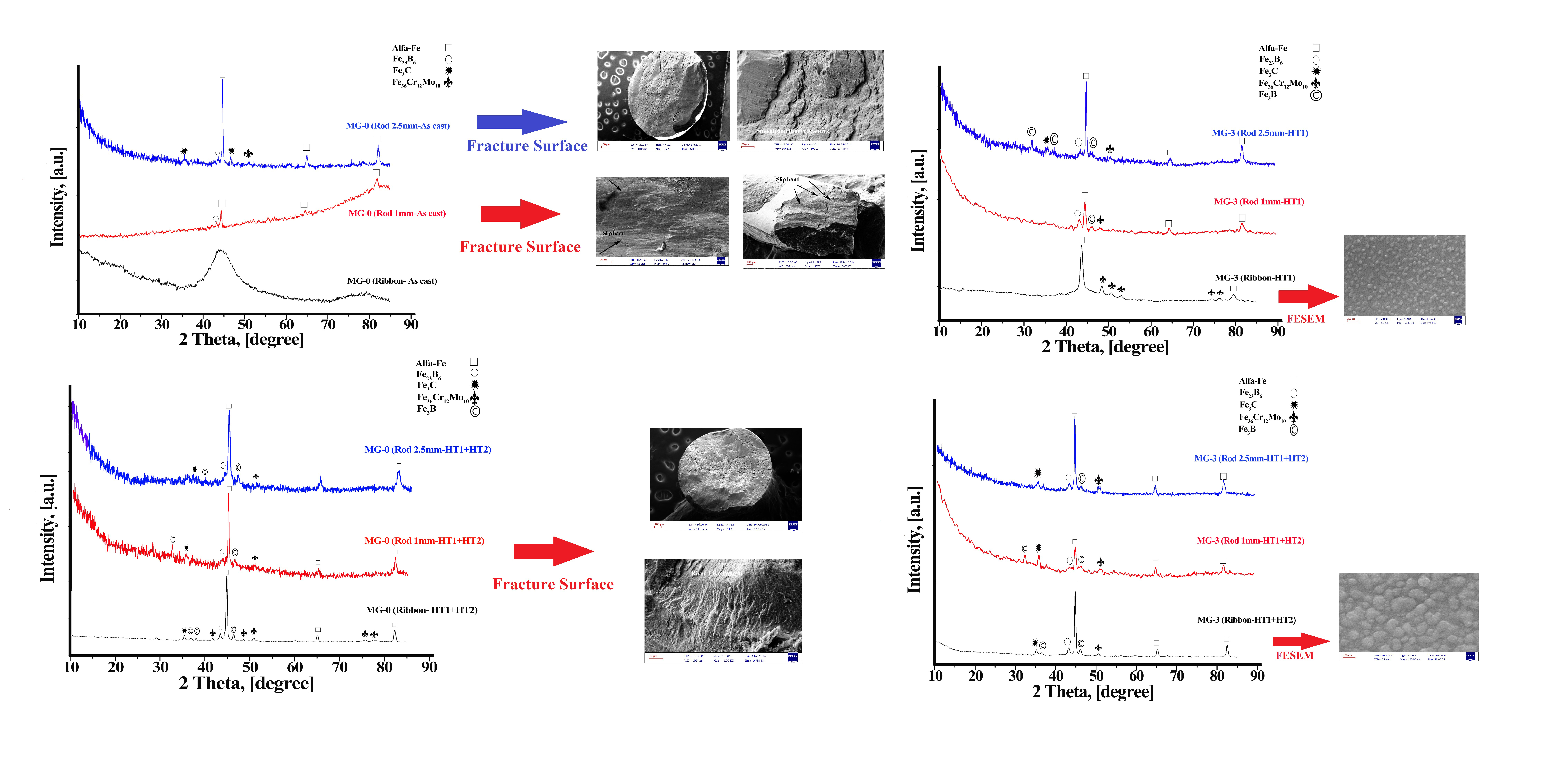
One-step and two-step annealing techniques were used to examine the relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties during compression tests in iron-based ribbons and nanostructured 1- and 2.5mm cylindrical rods. The X-ray diffraction, microstructural, and mechanical results showed that substituting Nb for Fe had a minor effect on glass-forming ability but increased the formability index. The novel two-step annealing process resulted in a remarkable formability index of 16.62 GPa, yield stress of 2830 MPa, ultimate strength of 3866 MPa, and 4.3% plastic strain. A ductile nanosized α-Fe framework and boron-containing nano precipitations, which caused Zener pinning effect, were responsible for these novel mechanical properties.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Ceramics
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |