Tue, Jan 28, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 21, Issue 2 (June 2024)
IJMSE 2024, 21(2): 53-69 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
V R, P S, A A. Numerical Optimization of Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction Synthesized Zinc Oxide Thin Film as Electron Transport Layer for Organic and Perovskite Solar Cells. IJMSE 2024; 21 (2) :53-69
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3463-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3463-en.html
Abstract: (6960 Views)
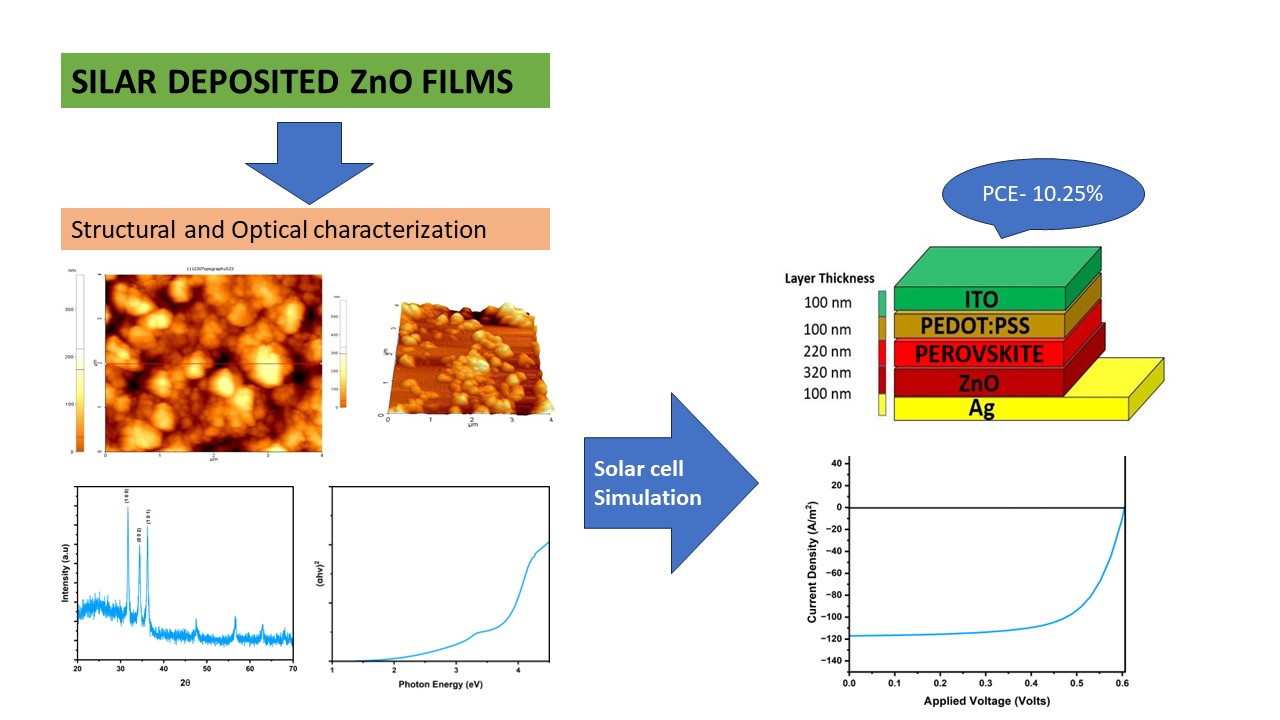
Organic and Perovskite solar cells have attracted a lot of attention recently since they can be used with flexible substrates and have lower manufacturing costs. The configuration and materials employed in their construction, including the Electron Transport Layer (ETL), active layer, electrode contact, and hole transport layer greatly influence the stability and performance of these solar cells. This research focuses on the simulation of solar cells, specifically utilizing zinc oxide (ZnO) as the electron transport layer. A 0.1 molar ZnO thin film was prepared from Zinc acetate salt and was deposited on a glass substrate using the cost effective Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction (SILAR) method. In-depth investigations were carried out on several factors, including structural, surface, optical and numerical analysis. The obtained parameters were utilized in the General-Purpose Photovoltaic Device Model (GPVDM) software to perform numerical simulations of the organic solar cell and Perovskite solar cell. Both Organic solar cells and Perovskite solar cells were designed numerically and through careful observations, electrical parameters like Open circuit Voltage (Voc), Short circuit current (Jsc), Fill Factor (FF), and Power Conversion Efficiency (PCE) were identified. The studies indicate the promising performance of simulated solar cells with SILAR-synthesized ZnO thin film as the ETL.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Synthesis and preparation of materials to meet the requirements of AM techniques
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |