Tue, Nov 5, 2024
[Archive]
Abstract: (1072 Views)
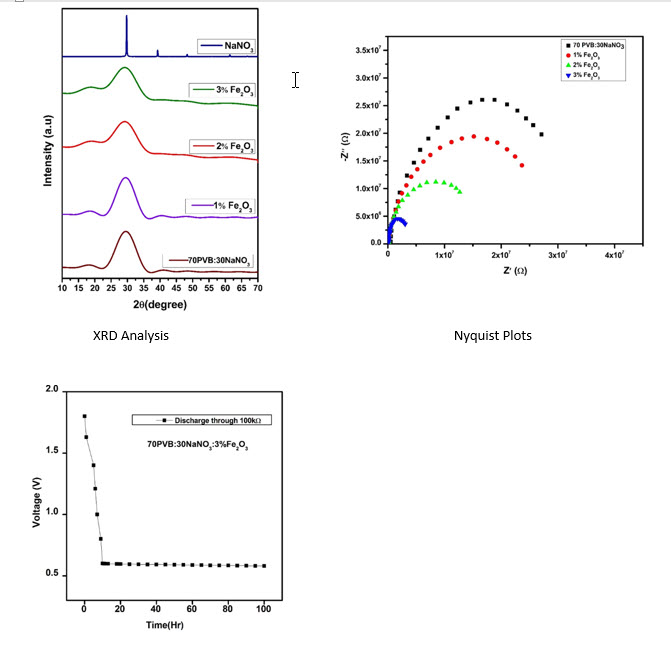
The composite solid polymer electrolyte films were prepared by doping nano-sized Fe2O3 particles on PVB (Polyvinyl Butyral) complexed with NaNO3 salt by solution casting technique. FTIR, XRD, and SEM methods characterized these electrolyte films. The Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction methods reveal the structural and complexation changes occurring in the electrolytes. The surface morphology of the electrolyte film was examined using the SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope) technique. The PVB+NaNO3+Fe2O3(70:30:3%) electrolyte shows a moderate ionic conductivity of 2.51×10−5 S cm−1 at ambient temperature (303 K). AC impedance spectroscopic analysis evaluates the ionic conductivity of the produced polymer electrolyte. Wagner's polarisation technique was applied to study the charge transport characteristics in the electrolyte films. The investigation revealed that ions constituted the majority of the transport carriers. An Open Circuit Voltage (OCV) of 2.0V and a Short Circuit Current (SCC) of 0.8 mA were found in the discharge characteristics data for the cell constructed with the polymer electrolyte sample.
Keywords: Polymer electrolytes, X-ray diffraction, Ionic conductivity, Discharge characteristics, Optical properties
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Polymers
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |