Tue, Mar 4, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 20, Issue 2 (June 2023)
IJMSE 2023, 20(2): 1-7 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Mohammed Hamoudi A, Choubani K, Ben Rabha M. Multicrystalline Silicon Passivation by Hydrogen and Oxygen- Rich Porous Silicon Layer for Photovoltaic Cells Applications. IJMSE 2023; 20 (2) :1-7
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-2908-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-2908-en.html
Abstract: (10675 Views)
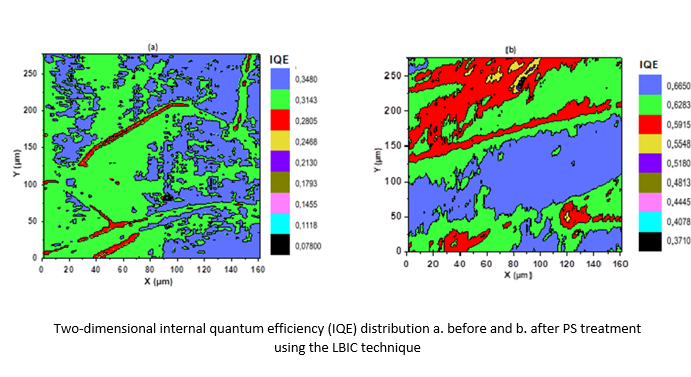
In this work, we demonstrate the beneficial effect of introducing a superficial porous silicon layer on the electronic quality of multi-crystalline silicon for photovoltaic cell application. The porous silicon was formed using an acid vapor etching-based method. The porous silicon layer rich in hydrogen and oxygen formed by vapor etching is an excellent passivating agent for the mc-Si surface. Laser beam-induced current (LBIC) analysis of the exponentiation parameter (n) and surface current mapping demonstrates that oxygen and hydrogen-rich porous silicon led to excellent surface passivation with a strong electronic quality improvement of multi-crystalline silicon. It was found that the generated current of treated silicon by acid vapor etching-based method is 20 times greater as compared to the reference substrate, owing to recombination centers passivation of the grains and grain boundaries (GBs); The actual study revealed an apparent decrease in the recombination velocity of the minority carrier as reflected by 25% decrease in the exponentiation parameter (n) of the LBIC versus X-position measurements. These results make achieved porous silicon a good option for advancing efficient photovoltaic cells.
Keywords: Multi-crystalline silicon, Laser beam induced current, Vapor etching, Oxygen and hydrogen, Passivation.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Casting and Solidification
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |